Whales as Oceanic Guardians: The Power of Whales as Carbon Sinks
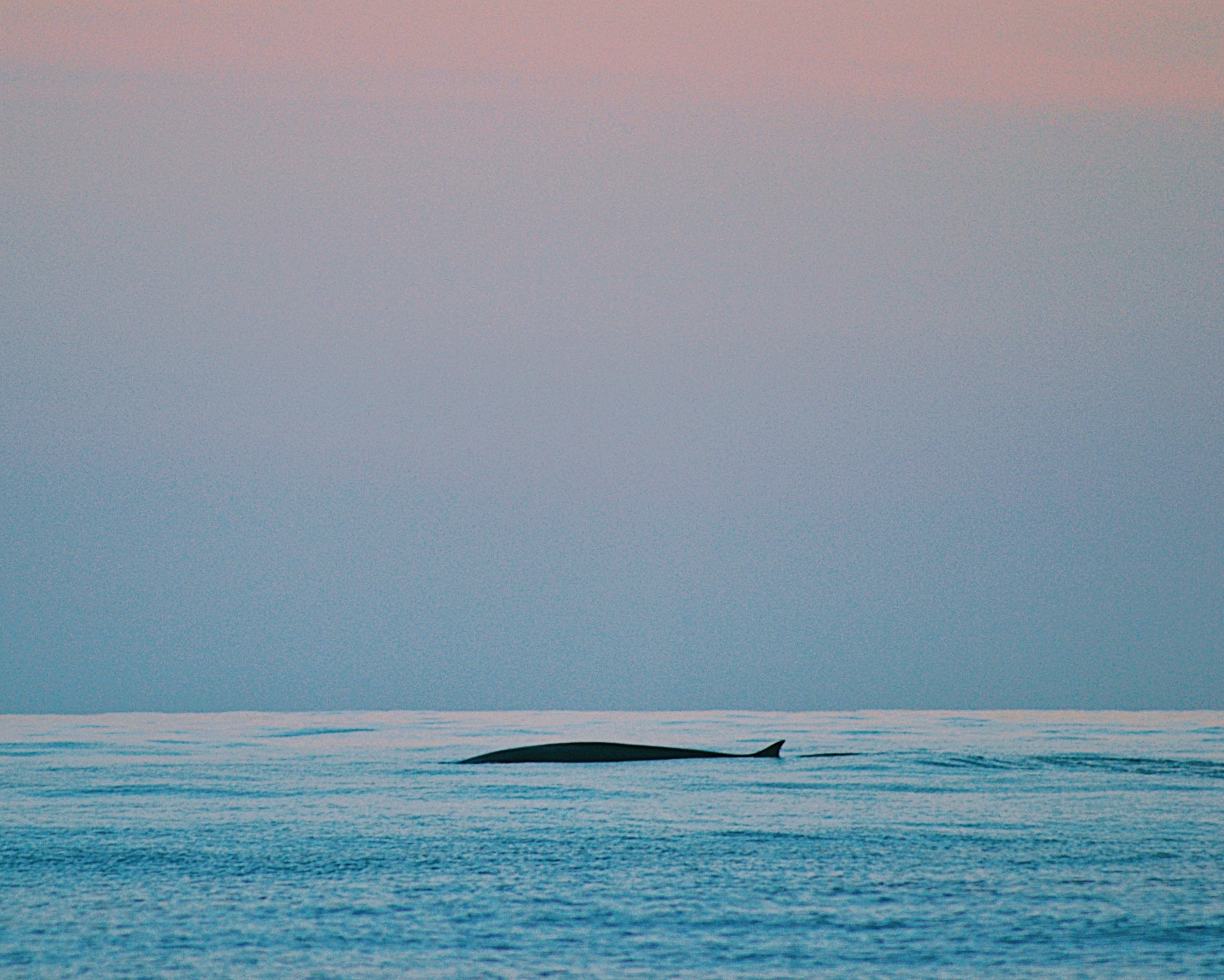
In the vast expanses of our oceans, a silent and majestic force is at play — one that not only captivates our imaginations but also plays a crucial role in mitigating the effects of climate change. Whales, the gentle giants of the sea, are emerging as unsung heroes in the fight against carbon emissions. Let’s explore the remarkable capacity of whales to act as oceanic guardians and potent carbon sinks.

- Understanding Carbon Sequestration: Carbon sequestration refers to the process by which carbon dioxide (CO2) is removed from the atmosphere and stored in natural reservoirs. Forests, soils, and the world’s oceans are among the essential carbon sinks that help regulate the global carbon cycle.
- The Whales’ Carbon Sequestration Role: Whales contribute to carbon sequestration through a fascinating chain of events. Their primary role lies in the oceanic realm, where they indirectly enhance the productivity of phytoplankton—the microscopic plants responsible for capturing carbon dioxide during photosynthesis.
- The Whale Pump: Fertilizing the Ocean: Whales play a pivotal role in what scientists refer to as the “whale pump.” When whales feed at depth, they consume large quantities of prey, effectively redistributing nutrients to surface waters through their excrement. This process acts as a fertilization mechanism, stimulating the growth of phytoplankton.
- Phytoplankton and Carbon Capture: As phytoplankton flourish in nutrient-rich surface waters, they engage in photosynthesis, drawing in CO2 from the atmosphere. This not only results in the creation of organic matter but also leads to the absorption and storage of carbon—a critical step in the fight against climate change.
- The Ripple Effect: A Cascade of Benefits: The enhanced presence of phytoplankton, fueled by the whale pump, initiates a cascade of benefits throughout the marine ecosystem. Increased phytoplankton supports diverse marine life, creating a thriving environment for fish and other organisms that depend on these microscopic plants.
- Protecting Whales for a Sustainable Future: Recognizing the invaluable contribution of whales to carbon sequestration underscores the urgency of protecting these marine giants. Conservation efforts, including the establishment of marine protected areas and measures to mitigate human-related threats like ship strikes and entanglement in fishing gear, are vital for securing the health and resilience of whale populations.
- Global Impact and Collective Responsibility: Whales, as carbon sinks, emphasize the interconnectedness of the global ecosystem. Preserving their populations and ensuring their continued contribution to carbon sequestration requires a collective effort. Governments, conservation organizations, and individuals all play a role in fostering responsible stewardship of our oceans.

As we navigate the complexities of climate change, whales emerge as powerful allies in our quest for sustainable solutions. Their unique role as carbon sinks, through the orchestration of the whale pump and the promotion of phytoplankton growth, showcases the profound impact that these marine giants have on our planet. Embracing and protecting whales is not only an investment in biodiversity but also a strategic move towards mitigating the impacts of climate change and preserving the delicate balance of our oceans.